Deep Learning: Transforming AI with Neural Networks
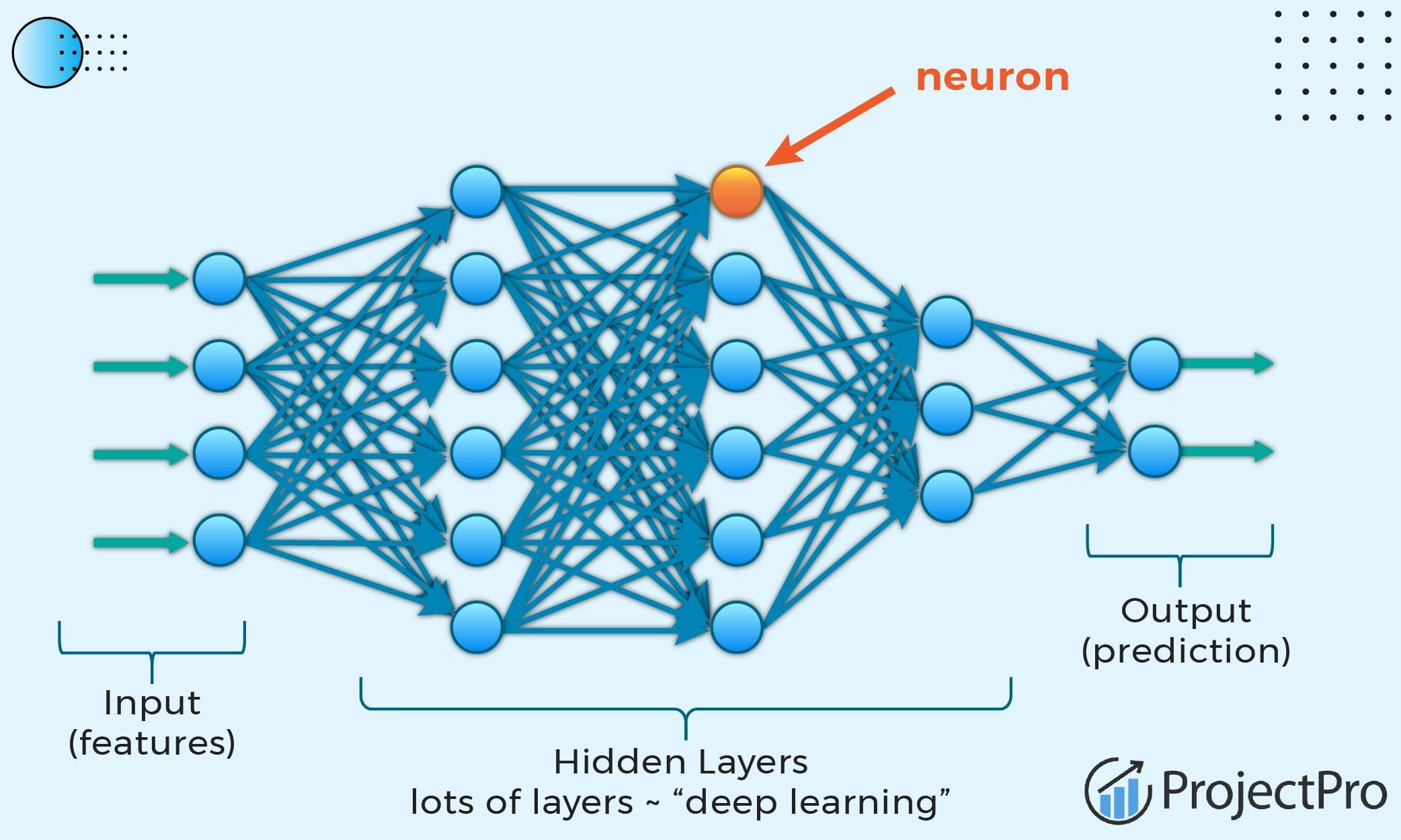
Deep learning represents a major shift in how artificial intelligence systems learn from data. Unlike traditional machine learning approaches that rely on manually engineered features, deep learning uses artificial neural networks to automatically discover complex patterns. By stacking multiple layers of neurons, these models learn hierarchical representations—progressing from simple features to highly abstract concepts.
This ability has made deep learning especially effective in domains where raw data is rich and unstructured.
Neural Architectures Powering Modern AI
At the core of deep learning are specialized neural network architectures designed for different types of data.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) excel at image and video analysis by capturing spatial patterns. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and their variants are suited for sequential data, enabling applications such as time-series analysis and speech processing. More recently, Transformer architectures have reshaped natural language processing by modeling long-range dependencies with attention mechanisms, setting new benchmarks across NLP tasks.
The Role of Data and Computational Power
Advances in deep learning have been closely tied to improvements in computational resources and data availability.
GPU acceleration has enabled the efficient training of large neural networks, while the availability of massive datasets has allowed models to generalize across diverse scenarios. Together, these factors have fueled rapid progress and made deep learning practical at scale.
Real-World Impact Across Industries
Beyond research, deep learning has become a foundational technology in many industries.
Applications range from medical image analysis and disease diagnosis to autonomous driving systems, speech recognition, and personalized recommendation engines. In each case, deep learning enables systems to process complex inputs and make informed decisions with high accuracy.
Challenges and Responsible Deployment
Despite its effectiveness, deep learning presents important challenges.
Training deep models requires careful architecture design, parameter tuning, and significant computational resources. Additionally, issues of interpretability, bias, and ethical use must be addressed to ensure reliable and responsible deployment—especially in high-stakes domains such as healthcare and autonomous systems.
Conclusion: A Cornerstone of Modern Artificial Intelligence
Deep learning has transformed artificial intelligence by enabling machines to learn directly from data at unprecedented levels of complexity. Its impact spans research and real-world applications alike.
As the field continues to evolve, success will depend not only on improving performance, but also on developing models that are transparent, efficient, and ethically aligned. Deep learning is not just a tool for smarter systems—it is a foundation for the future of AI.
References










